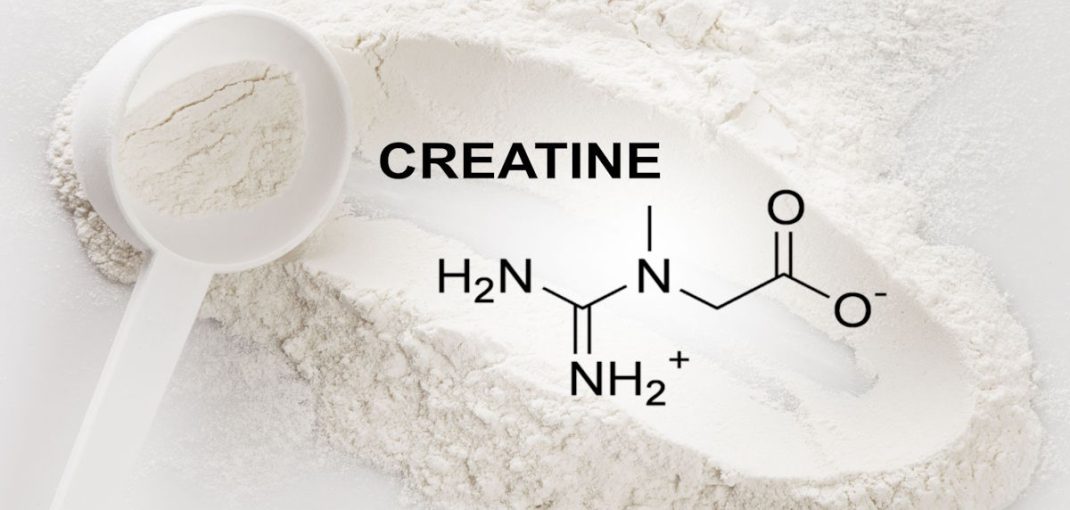
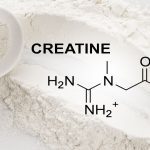
Hello fitness enthusiasts, body sculptors, and those just trying to keep their New Year’s resolution alive! Today, we’re diving into the world of one of the most researched, debated, and celebrated supplements out there: Creatine. Buckle up, because we’re about to explore why this little molecule is a big deal.
Creatine is one of the most widely used and researched supplements in the fitness industry. Known for its ability to enhance muscle growth and improve workout performance, creatine is a staple for many athletes and fitness enthusiasts. This guide will delve into the benefits, myths, usage, and best practices for incorporating creatine into your fitness regimen.
Common Myths Debunked
There are several misconceptions about creatine that often deter people from using it. Let’s address and debunk some of these myths:
- Creatine is a steroid: This is a common misconception. Creatine is not a steroid; it is an organic compound that occurs naturally in the body and in foods like red meat and fish. It helps supply energy to cells, particularly muscle cells.
- Creatine is only for bodybuilders: While bodybuilders do benefit significantly from creatine, it is also beneficial for a wide range of athletes, including those involved in high-intensity sports like sprinting, football, and weightlifting.
- Creatine damages kidneys: Numerous studies have shown that creatine is safe for healthy individuals. However, those with pre-existing kidney conditions should consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation.
- Creatine causes bloating: Some users report minor water retention when they first start taking creatine, but this effect is usually temporary and minimal.
- You need to cycle creatine: Unlike some supplements, creatine does not need to be cycled. Consistent daily supplementation is both safe and effective for long-term use.
How Creatine Works
Creatine works by increasing the availability of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy carrier in cells. During high-intensity exercise, ATP is rapidly depleted. Creatine helps replenish ATP, allowing for improved performance, increased strength, and enhanced endurance. There are several forms of creatine available, including:
- Creatine Monohydrate: The most researched and widely used form.
- Creatine HCL (Hydrochloride): Known for better solubility and absorption.
- Creatine Ethyl Ester: Marketed
for its potential to reduce water retention.
Benefits of Creatine
Creatine offers a multitude of benefits beyond just muscle growth. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Muscle Magic
First off, creatine is like the fairy godmother of muscle growth. It helps in the production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is basically the energy currency your muscles use for those soul-crushing squats or that one more rep that feels like you’re lifting the earth itself. More ATP means more explosive power, better performance, and, you guessed it, muscle growth. - The Hydration Hero
One lesser-known fact is that creatine pulls water into your muscle cells, making them swell like balloons on a helium binge. This isn’t just for show; it can lead to an increase in muscle volume, which might not only make you look like you’ve been hitting the gym harder than you actually have, but also can enhance muscle performance by improving cell hydration. - Brain Gain
Surprise! Creatine isn’t just for your biceps. Studies suggest it might even give your brain a boost. Yes, you read that right. Increased creatine levels in the brain could enhance cognitive functions like memory and intelligence. Think of it as a smart drug for your muscles and your mind. Who said you couldn’t be both strong and smart? - Recovery Road
Ever felt like your muscles were staging a revolt the day after leg day? Creatine might just be your peace treaty. By aiding in quicker recovery, it reduces muscle cell damage and inflammation. This means you can say goodbye to those “I can’t even walk” days and hello to more consistent workouts. - The Aging Antidote
As we age, our muscles start to throw a tantrum, decreasing in size and strength. Creatine supplementation has been shown to combat this age-related muscle loss, helping you maintain that youthful vigor. It’s like a time machine for your muscles, minus the risk of running into your younger self at the gym. - Bone Density Booster
And here’s a plot twist for you: creatine might just be good for your bones too. Some research indicates an increase in bone mineral density with creatine use, which is particularly beneficial for women post-menopause. Now, you can lift weights and strengthen your bones at the same time. Talk about efficiency!
Dosage and Timing
Proper dosing and timing are crucial to maximizing the benefits of creatine. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Loading Phase: To quickly saturate your muscles with creatine, start with a loading phase of 20 grams per day, divided into 4 doses, for 5-7 days.
- Maintenance Phase: After the loading phase, switch to a maintenance dose of 3-5 grams per day. If you are over 225 pounds then an 8 gram dosage may be more effective.
- Best Time to Take: There is no specific time that is universally best for taking creatine. The key is consistency. Some prefer taking it post-workout to aid recovery, while others take it pre-workout for an energy boost.
Stacking and Hydration
Creatine can be effectively combined with other supplements to enhance its benefits:
- Beta-Alanine: This amino acid can help buffer acid in muscles, improving endurance.
- Caffeine: Known for its stimulant effects, caffeine can complement creatine by enhancing focus and energy levels.
Hydration is also critical when taking creatine. Ensure you drink plenty of water throughout the day to prevent dehydration and muscle cramps, as creatine can increase water retention in muscles.
Creatine is not just a supplement; it’s a lifestyle choice for those looking to push their physical and mental limits. From enhancing muscle performance to possibly making you smarter, creatine is the Swiss Army knife of supplements. So, if you’re looking to optimize your body’s performance, consider giving creatine a spot in your supplement stack. Just remember, with great power comes great responsibility – use it wisely, and may your gains be plentiful!
Happy lifting, brain boosting, and aging gracefully with creatine! Note: Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new supplement regimen.